A DISPLAY OF DIGITAL MANUFACTURING TECHNIQUES

During this workshop, we practised a long pipeline: translating a 3D scan into 6 different manufacturing techniques.
During the first week, the entire studio scanned a 49:er sail boat in the Aarhus harbour with a Faro FOCUS 3D. A straight forward action which mainly involves meticulous work and patience. We assembled the scans in Geomagic Wrap 2014 and meshed them. The mesh was split into 6 parts. Each group of 3 manufacturing their piece with a specific digital manufacturing technique.
I worked with Nils Fröhling, Liam Marosy-Weide and Alexandria Chan. We were assigned hot wire cutting with the small ABB IRB 120 robot. Because of the complexity of the mesh, I had to remodel our piece of the boat in Rhino. We split it in several small pieces to enable cutting with the small robot and re-modelled every piece into ruled surfaces. Since the robot didn’t have enough range to cut our pieces on all sides, we designed and welded an addition to it. A steel cantilever support which you can see further down on the page, to enable the robot to be mounted on the side of the table. In order to add an extra bit of spice, we decided to translate the cut foam assembly into a shell of fibre glass with carbon fibre strands: tattooing the boat with it’s major stress lines caused by it’s movement in the water.
In the end, the entire boat (now in scale 1:2) was exhibited in the Aarhus Architecture School cantine to show the student body the full range of the digital manufacturing techniques of the school.
Manufacturing techniques from right back: Planar manufacturing (plastic sheets using the Zünd digital cutter), 5 axis manufacturing (wood using a 5 Axis CNC Machine Center), 5 axis manufacturing (foam using the ABB IRB 6620 robot), planar manufacturing (plexi and cardboard using a Ez laser LCW 140dD), 3D printing (PLA using a Ultimaker 2) and hot wire cutting (foam using a ABB IRB 120 robot).
Photograph: Grant Davis Edit: Me, Photoshop
During the first week, the entire studio scanned a 49:er sail boat in the Aarhus harbour with a Faro FOCUS 3D. A straight forward action which mainly involves meticulous work and patience. We assembled the scans in Geomagic Wrap 2014 and meshed them. The mesh was split into 6 parts. Each group of 3 manufacturing their piece with a specific digital manufacturing technique.
I worked with Nils Fröhling, Liam Marosy-Weide and Alexandria Chan. We were assigned hot wire cutting with the small ABB IRB 120 robot. Because of the complexity of the mesh, I had to remodel our piece of the boat in Rhino. We split it in several small pieces to enable cutting with the small robot and re-modelled every piece into ruled surfaces. Since the robot didn’t have enough range to cut our pieces on all sides, we designed and welded an addition to it. A steel cantilever support which you can see further down on the page, to enable the robot to be mounted on the side of the table. In order to add an extra bit of spice, we decided to translate the cut foam assembly into a shell of fibre glass with carbon fibre strands: tattooing the boat with it’s major stress lines caused by it’s movement in the water.
In the end, the entire boat (now in scale 1:2) was exhibited in the Aarhus Architecture School cantine to show the student body the full range of the digital manufacturing techniques of the school.
Manufacturing techniques from right back: Planar manufacturing (plastic sheets using the Zünd digital cutter), 5 axis manufacturing (wood using a 5 Axis CNC Machine Center), 5 axis manufacturing (foam using the ABB IRB 6620 robot), planar manufacturing (plexi and cardboard using a Ez laser LCW 140dD), 3D printing (PLA using a Ultimaker 2) and hot wire cutting (foam using a ABB IRB 120 robot).
Photograph: Grant Davis Edit: Me, Photoshop
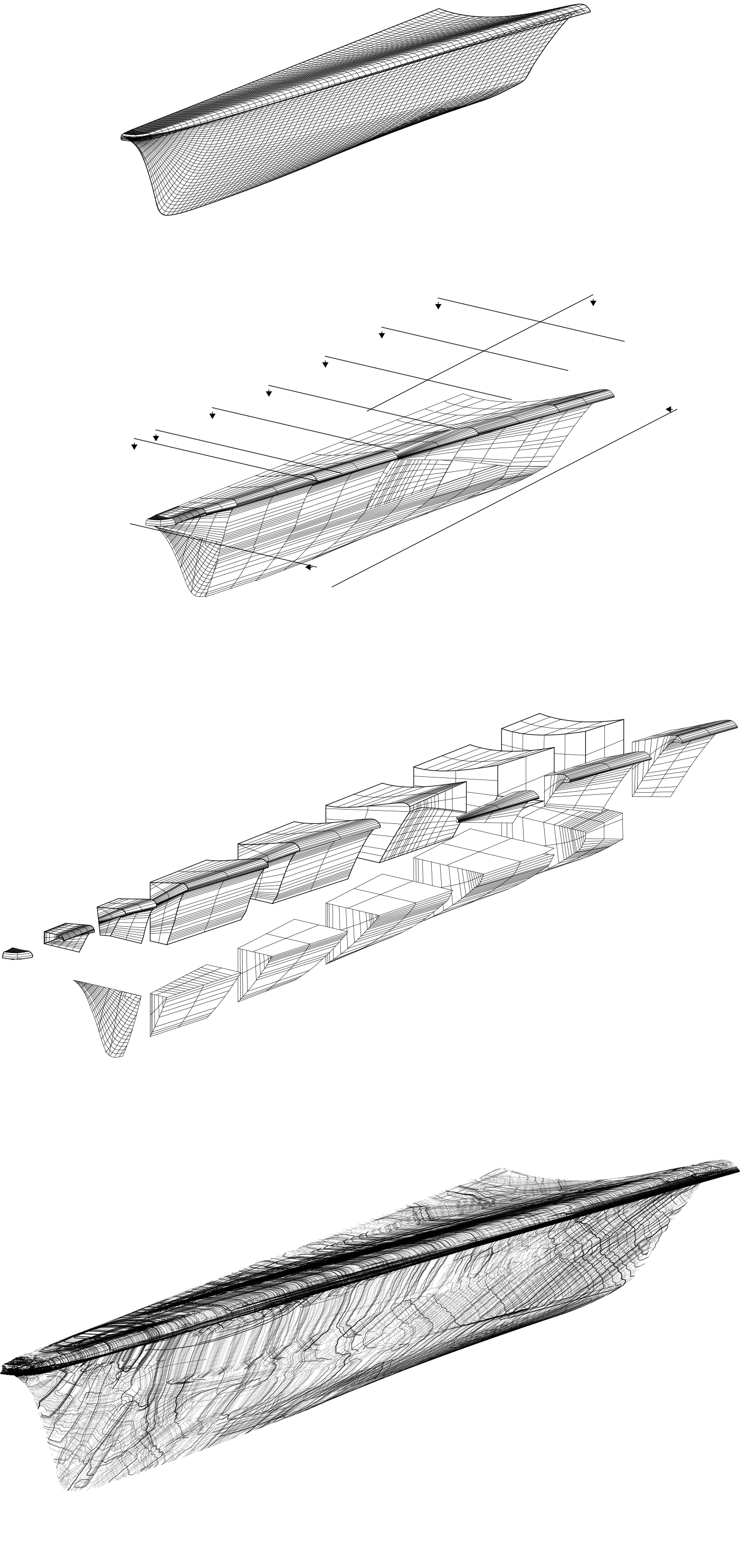
3 top images: Pieces remodelled to straight sections. Modelling: Rhino.
4th image: Stress analysis. Analysis: Grasshopper using Millipede.
4th image: Stress analysis. Analysis: Grasshopper using Millipede.
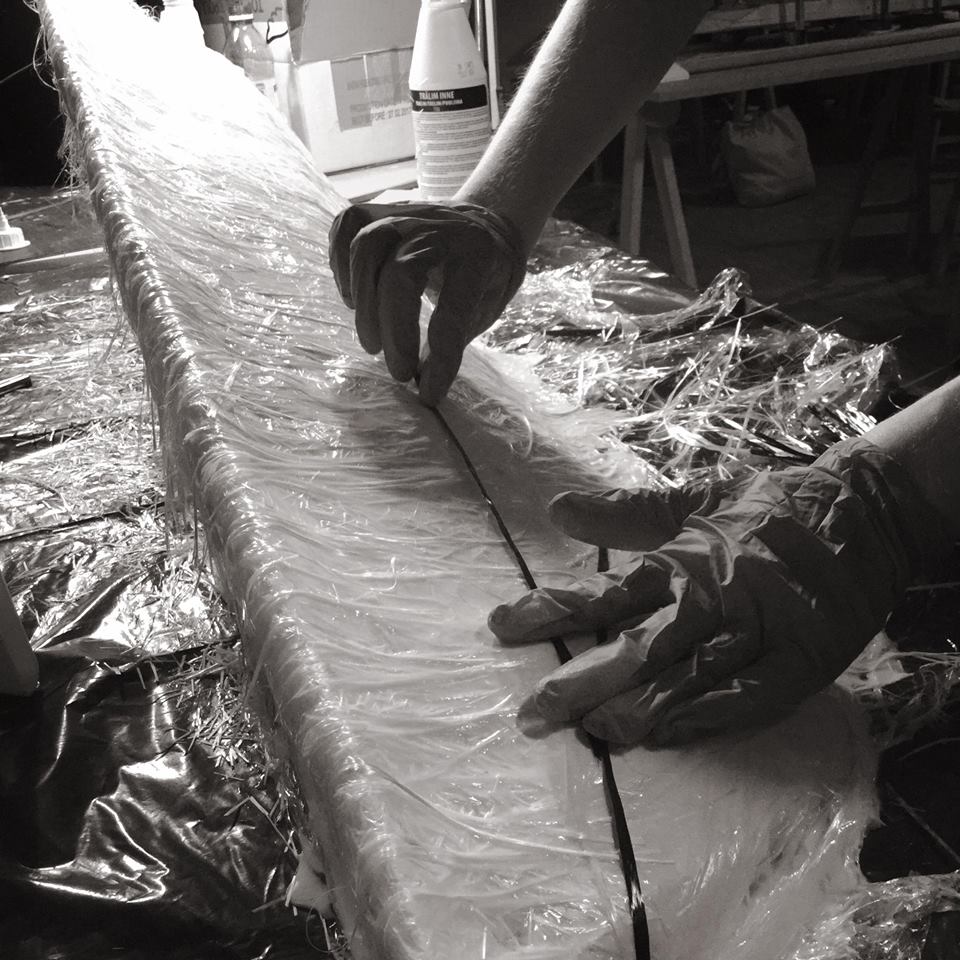

Me layering fiber glass and glue.
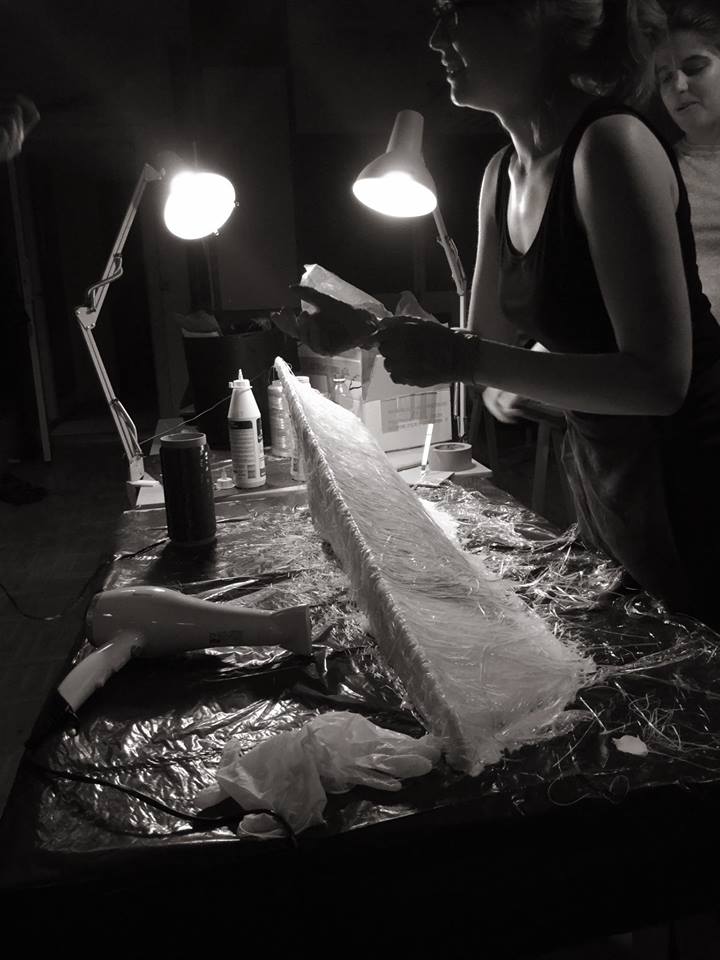

Me layering fiber glass and glue.
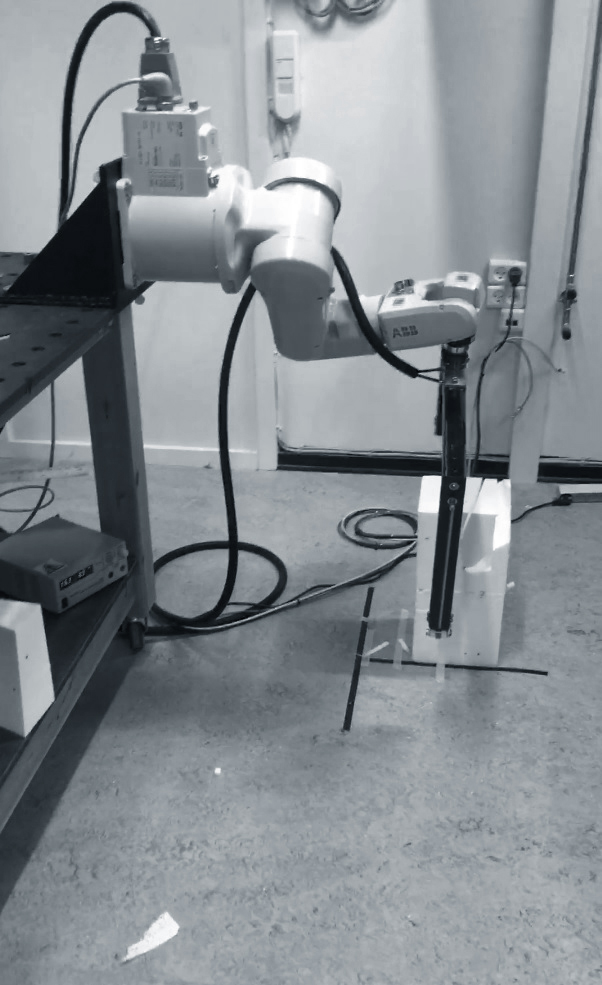
The small ABB IRB 120 robot, in action mounted
on our cantilever support.
on our cantilever support.
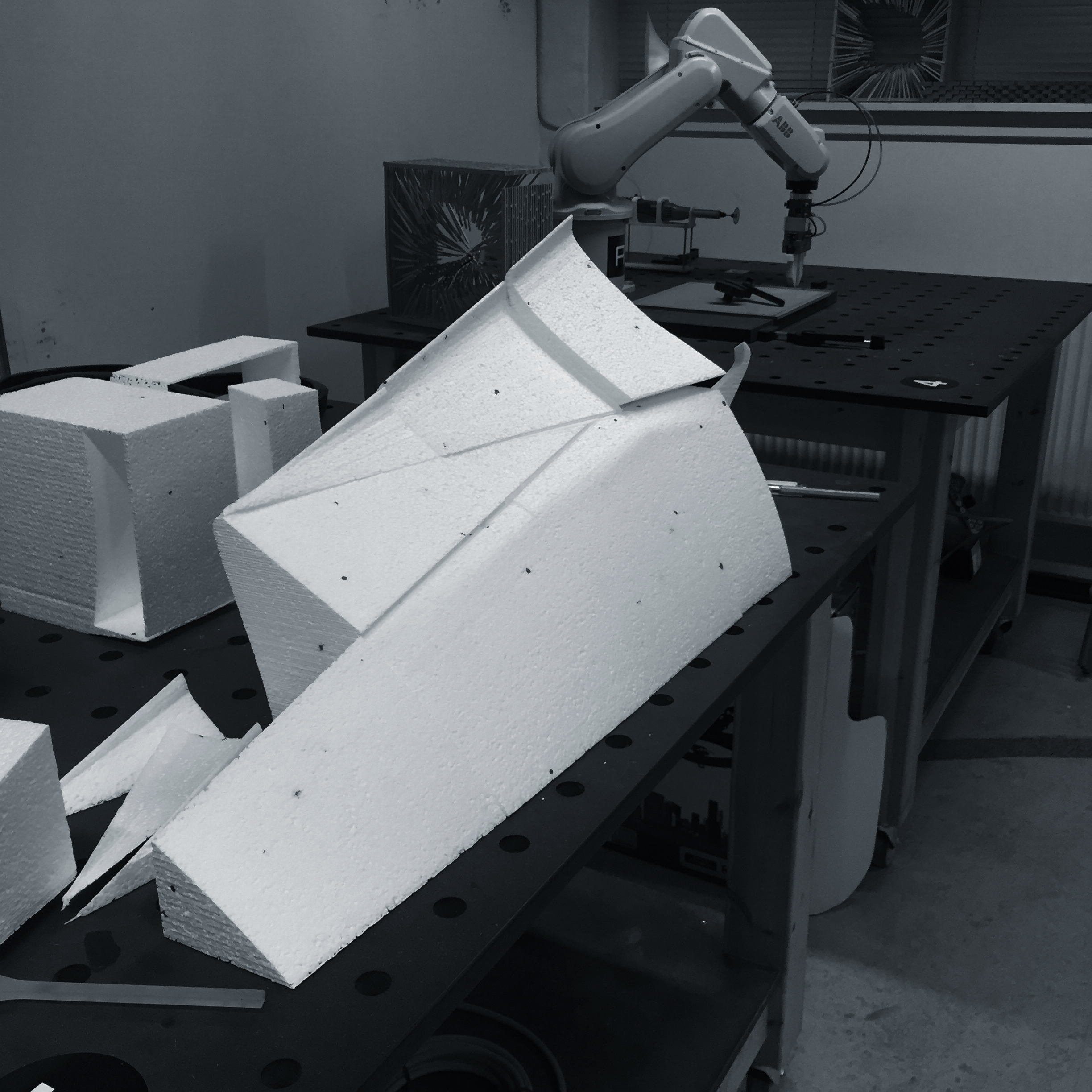

Assembly of foam pieces in action.
A workshop at the Aarhus school of Architecture – Digital manufacturing techniques.